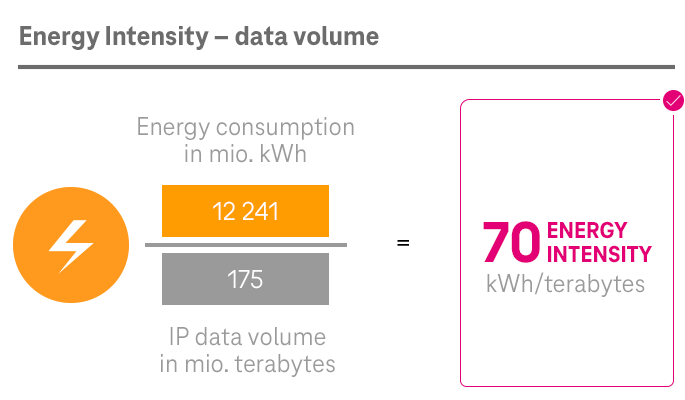
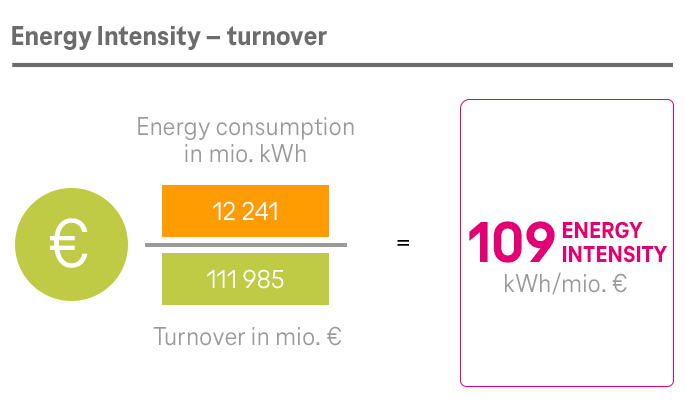
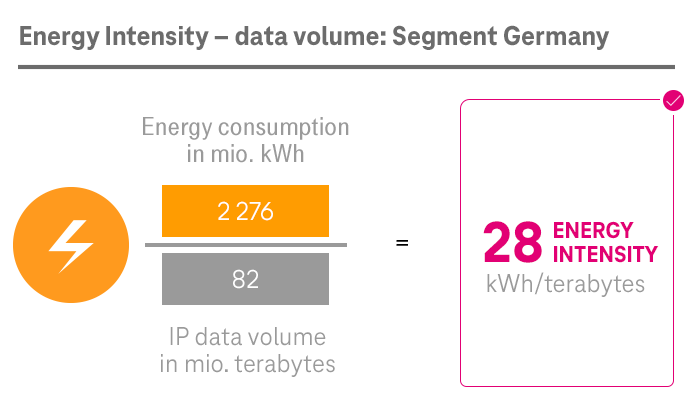
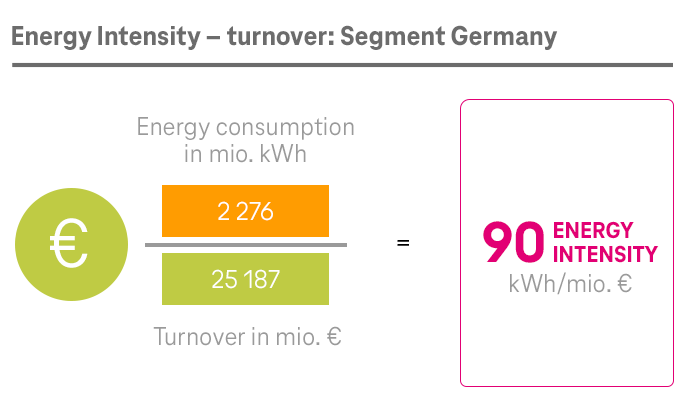
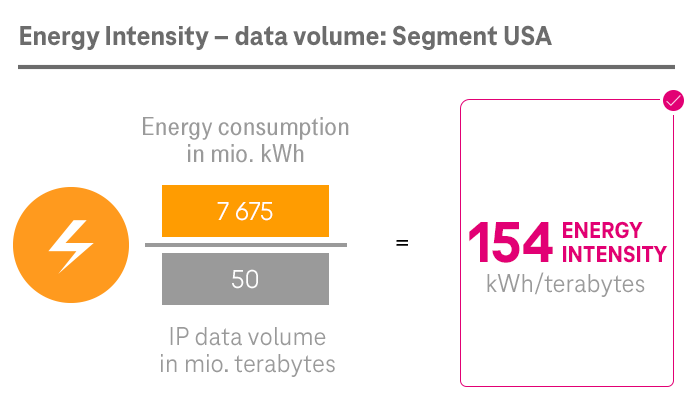
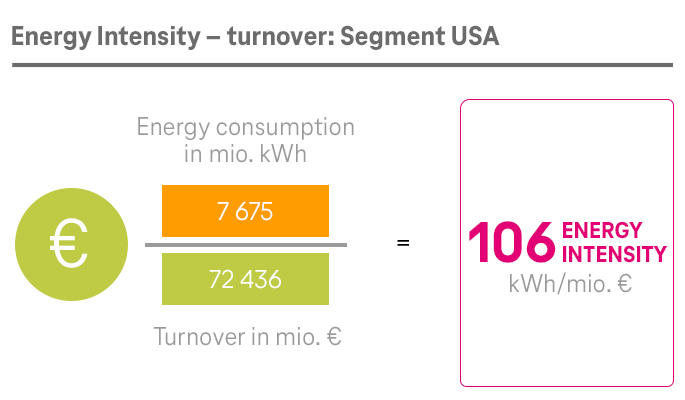
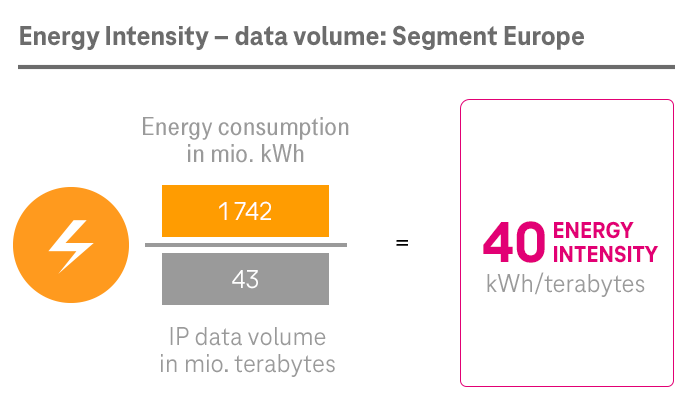
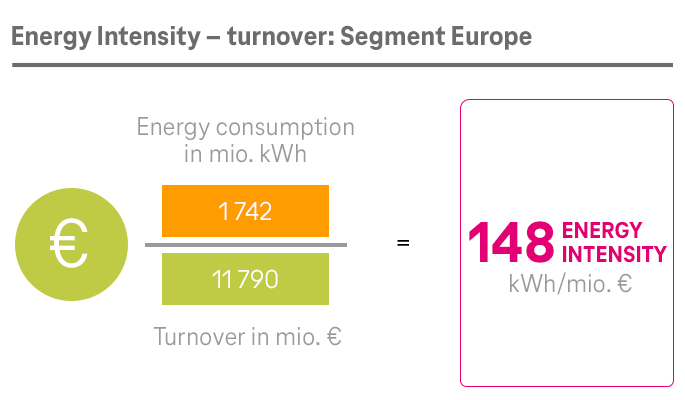
As part of Deutsche Telekom, the System Solutions segment has also committed itself to the Group-wide climate targets. The segment set up its own program to this end in 2020, with a focus on two areas: its own processes on the one hand and its product offering and business customer enablement on the other.
Data center energy efficiency
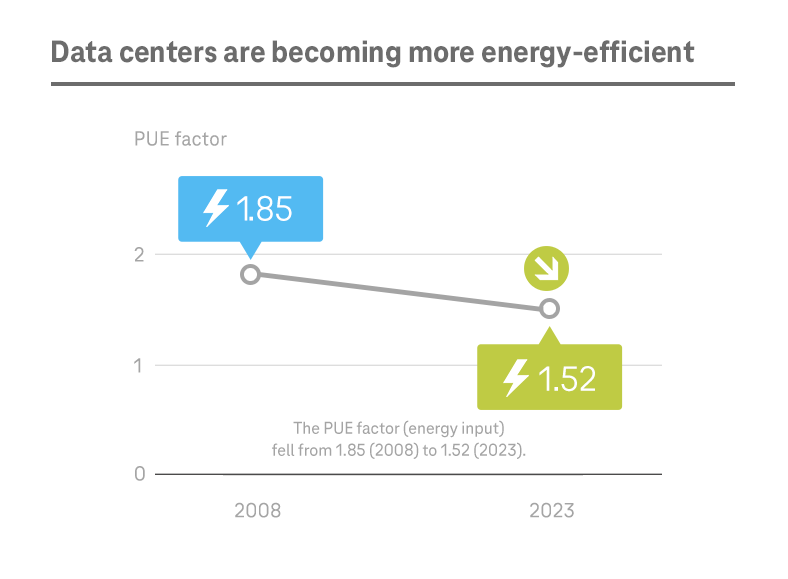
T-Systems is gradually making its data centers more energy-efficient, with the aid of innovative technologies and artificial intelligence. As an operator, T-Systems is careful to use energy-efficient server and storage hardware. As part of its Data Center Next program, launched in 2019, it is making use of efficiency-enhancing measures, such as selective cooling of individual areas, and operating temperature increases within possible ranges – always in conformance with defined thresholds. Testing is being carried out with regard to gradually raising the operating temperature at data centers, with a one degree increase corresponding to an energy efficiency gain of approximately 1 percent. Software features which allow unused hardware to be switched off entirely without affecting currently running applications will be used for further optimizations. The medium- to long-term goal is to refine the cloud applications to meet energy efficiency requirements (green coding). T-Systems continue to work on optimizing energy efficiency in all data centers. Since launching the Data Center Next program, we have already reduced energy consumption in our data centers by over 37 percent.
T-Systems has participated in the EU Code of Conduct on Data Centre Energy Efficiency (EU DC CoC) since 2014. EU DC CoC is voluntary in nature and aims to motivate operators and owners of data centers to reduce energy consumption and hence their negative impact on the environment, the economy, and energy supply security. The initiative refers to this type of involvement as “participation.” The related European Commission page provides transparent, detailed information about the participation of individual data centers. T-Systems also joined the Climate Neutral Data Centre Pact (CNDCP) in 2021. With this move, it has committed to making all of its own data centers, and the externally operated data centers within its sphere, climate neutral by 2030 at the latest. T-Systems were certified as an official member by the CNDCP in 2023, following an audit  of the following five areas: energy efficiency, renewable energy use, water efficiency, circular economy for electronics, and circular economy for heat. T-Systems’ data centers around the world have been running on 100 percent renewable energy since 2021. To this end, renewable energy is sourced directly wherever it is available. Where this is not possible electricity requirements are covered by concluding power purchase agreements (PPAs
of the following five areas: energy efficiency, renewable energy use, water efficiency, circular economy for electronics, and circular economy for heat. T-Systems’ data centers around the world have been running on 100 percent renewable energy since 2021. To this end, renewable energy is sourced directly wherever it is available. Where this is not possible electricity requirements are covered by concluding power purchase agreements (PPAs  ), generating our own energy, or purchasing guarantees of origin. You can find more information on renewable energy at Deutsche Telekom here.
), generating our own energy, or purchasing guarantees of origin. You can find more information on renewable energy at Deutsche Telekom here.
The European Commission presented the T-Systems data center in Biere with the European Code of Conduct Award in 2023. The award recognized the data center for its PUE  score, best practices and energy-efficiency methods, among other things. With a PUE of 1.3, the data center in Biere is one of the most energy-efficient in Europe.
score, best practices and energy-efficiency methods, among other things. With a PUE of 1.3, the data center in Biere is one of the most energy-efficient in Europe.
At the end of 2023, T-Systems operated a total of 16 FMO (Future Mode of Operation) twin-core data centers in Europe at eight sites – eight for internal and eight for external processing – in addition to four local customer-specific data centers. Seven of the eight internal European FMO twin-core data centers, plus one external FMO twin-core data center, have been included in the EU Code of Conduct list since 2023. By taking part in the “EU Code of Conduct”, T-Systems meets an important criterion for achieving taxonomy alignment under the EU Taxonomy  for sustainable activities (EU Taxonomy). More information about the commitment within the framework of the EU Taxonomy is available here.
for sustainable activities (EU Taxonomy). More information about the commitment within the framework of the EU Taxonomy is available here.
Raising awareness among employees
The company’s employees, at all of its production sites and in all countries in which it is located, are being made more aware of the need to think and act with sustainability in mind ( for instance, by promoting alternative mobility solutions, participating in “campaign days” focused on sustainability, participating in sustainability-oriented workshops, and providing information about ways to reduce power and resource consumption). The susTain Roadshow was held for the first time during the year under review, with 120 colleagues in four German cities using the opportunity to find out about T-Systems’ sustainability activities. There were presentations as well as opportunities for attendees get involved.
These activities were supplemented by an open call to raise awareness of sustainability issues among employees around the world as well. 377 participants dialed in to learn more and engage in dialog. We also ran formal dialog events and smaller learning units with our international subsidiaries in which we provided information on sustainability and support for implementing the measures locally.
T-Systems supports relevant employee initiatives, such as the Green Pioneers in Germany. Moreover, Sustainability is an integral part of the onboarding program for all new T-Systems employees. An employee training course was developed in 2022 to train up staff members as sustainability ambassadors. Over 600 employees have already completed the course. In the year under review, T-Systems and Deutsche Telekom began to develop a digital Deutsche Telekom Sustainability Campus for all employees, which will comprise three competence levels. The first module is set to be made available during the first six months of 2024.
Expanding the green fleet
In January 2023, Deutsche Telekom issued an internal directive in Germany to only order company cars with electric drive systems going forward. This requirement has been applicable internationally for the Systems Solutions segment since 2022. T-Systems had a total of 1 959 company cars in its fleet at the end of 2023, 382 of which were electric vehicles. At this same time, most of our Meet & Connect Hubs had been fitted with charging stations. Meet & Connect Hubs are the central locations of T-Systems and are designed to offer the ideal environment for working in teams. They provide collaboration rooms and innovative spaces that cover a whole range of requirements and uses.
More sustainable buildings
T-Systems was able to reduce its building capacity in Germany by more than half during the year under review, which also reduced heating and district heating. T-Systems also plans to offset CO2 emissions through the use of neutralization technologies such as vertical farming, with a pilot project set to launch at its data center site in Biere in 2024.